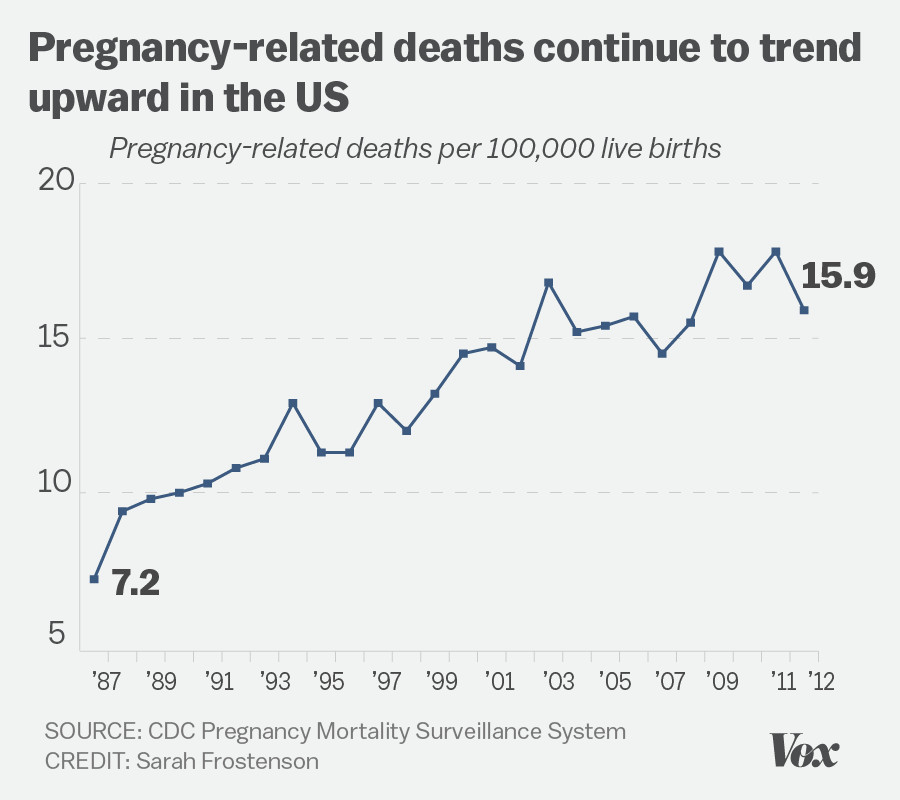
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are a growing concern as recent studies reveal an alarming rise in the maternal mortality rate across the nation. Despite the fact that over 80% of these tragic fatalities are considered preventable, the United States continues to lead high-income countries with the highest rates of pregnancy-related deaths. From 2018 to 2022, significant disparities emerged across different states, races, and ethnicities, with barriers to adequate postpartum care exacerbating the situation. Moreover, the COVID-19 impact on pregnancy has intensified these challenges, highlighting the urgent need for systemic changes in maternal health policies. Addressing the preventable aspects of maternal mortality is essential to ensure that every expecting mother receives equitable healthcare throughout their pregnancy journey.
In the realm of maternal health, the alarming trend of increasing pregnancy-related fatalities in the U.S. underscores critical issues plaguing the healthcare system. Often overshadowed by other health priorities, the importance of addressing maternal health disparities and the factors influencing maternal mortality cannot be overstated. Recent findings indicate not only the high incidence of avoidable pregnancy deaths but also illuminate the racial and state-level disparities that persist from prenatal care through postpartum recovery. With a comprehensive view of these challenges, it is crucial to advocate for improved healthcare access and innovative solutions aimed at reducing the maternal mortality rate, thus ensuring safe pregnancy experiences for all women.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The increasing rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. have become a concerning trend, particularly as data reveals a staggering 80 percent of these deaths are preventable. With the nation grappling with the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, it’s critical to examine the systemic issues at play. Factors contributing to this alarming statistic include inadequate access to comprehensive prenatal care and disparities in healthcare based on race and ethnicity.
A recent study uncovered that American Indian and Alaska Native women are disproportionately affected, experiencing maternal mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. This discrepancy underlines the urgent need for targeted interventions and better-infrastructured healthcare systems that not only consider pregnancy outcomes but also the long-term health of mothers in the critical first year postpartum.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the leading causes of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
In the U.S., cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of these fatalities. Other significant contributors include hemorrhage and complications from chronic conditions like hypertension. Understanding these causes is crucial for reducing the maternal mortality rate.
How do racial disparities in maternal health contribute to U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Racial disparities significantly impact U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest mortality rates. Factors contributing to these disparities include inequitable access to quality healthcare, systemic discrimination, and socioeconomic status, highlighting the urgent need to address these inequities.
Why are many U.S. pregnancy-related deaths considered preventable?
Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are deemed preventable through improved healthcare practices, education, and access to appropriate prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing these preventable deaths requires a focus on healthcare system reform and enhanced maternal health policy.
What impact did COVID-19 have on U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 correlated with a significant rise in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, with the sharpest increases observed in 2021. The pandemic affected healthcare access and resource allocation, contributing to higher maternal mortality rates during this period.
How does postpartum care influence U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is critical in reducing U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, as nearly one-third of maternal fatalities occur between 42 days to one year post-pregnancy. Comprehensive healthcare during this extended postpartum period is vital for monitoring and managing potential complications.
What measures can be taken to reduce the maternal mortality rate in the U.S.?
To reduce the maternal mortality rate, investments in public health infrastructure, innovative quality of care interventions for pregnancy and postpartum periods, and policy reforms to address state-level disparities are necessary. Enhancing access to full-spectrum maternal health services is critical.
What role does the maternal mortality rate play in evaluating U.S. healthcare quality?
The maternal mortality rate serves as a vital indicator of healthcare quality, reflecting systemic issues within the healthcare system. A high maternal mortality rate suggests deficiencies in prenatal and postpartum care, as well as broader social determinants of health affecting vulnerable populations.
How do states vary in their rates of pregnancy-related deaths?
There is significant variation in pregnancy-related death rates across different U.S. states, ranging from 18.5 to 59.7 deaths per 100,000 live births. This disparity points to unequal healthcare access and quality, underscoring the need for targeted interventions to improve outcomes in high-risk areas.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has seen a steady increase in maternal mortality rates, with 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, up from 25.3 in 2018. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, indicating a need for better healthcare strategies. |
| Racial Disparities | Significant disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates of maternal mortality. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the situation, particularly in 2021 when death rates peaked. |
| Need for Extended Care | There is a strong call for improved prenatal and postpartum care, extending support beyond traditional timeframes. |
| Public Health Infrastructure | Investment in public health infrastructure is crucial to combat the rise in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are a growing concern, with rising rates that highlight systemic failures in maternal healthcare. Despite being preventable in many cases, these deaths underscore the urgent need for effective interventions, equitable healthcare practices, and comprehensive support systems for expecting and new mothers. Addressing these issues could save lives and improve maternal health outcomes across the nation.