Bile acid metabolism is a crucial process that plays a significant role in the maintenance of liver health and overall metabolic balance. It has been increasingly recognized that an imbalance in bile acids can have dire consequences, such as contributing to the development of liver diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. Recent research highlights the importance of regulating this metabolism through the FXR receptor, which is essential for bile acid homeostasis. These findings may open new avenues for liver cancer treatment, particularly by targeting pathways like the YAP signaling pathway that influence bile acid levels. Understanding how these interconnected systems contribute to liver health is vital for developing effective interventions against liver-related conditions.
The intricate processes of bile acid metabolism, the biochemical pathways that facilitate the synthesis and regulation of bile acids, play a pivotal role in liver physiology. This metabolic pathway becomes increasingly relevant when considering its implications for serious liver conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma, the leading type of liver cancer. Innovative research indicates that disruptions in bile acid homeostasis may be linked to the activation of specific cellular signals, including those mediated by the FXR receptor and YAP signaling pathway. These connections unveil a potential therapeutic landscape for liver cancer treatment, focusing on restoring balance in bile acids. As scientists delve deeper into the roles these compounds and pathways play, new strategies for combating liver diseases are expected to emerge.
Understanding Bile Acid Metabolism and Liver Function
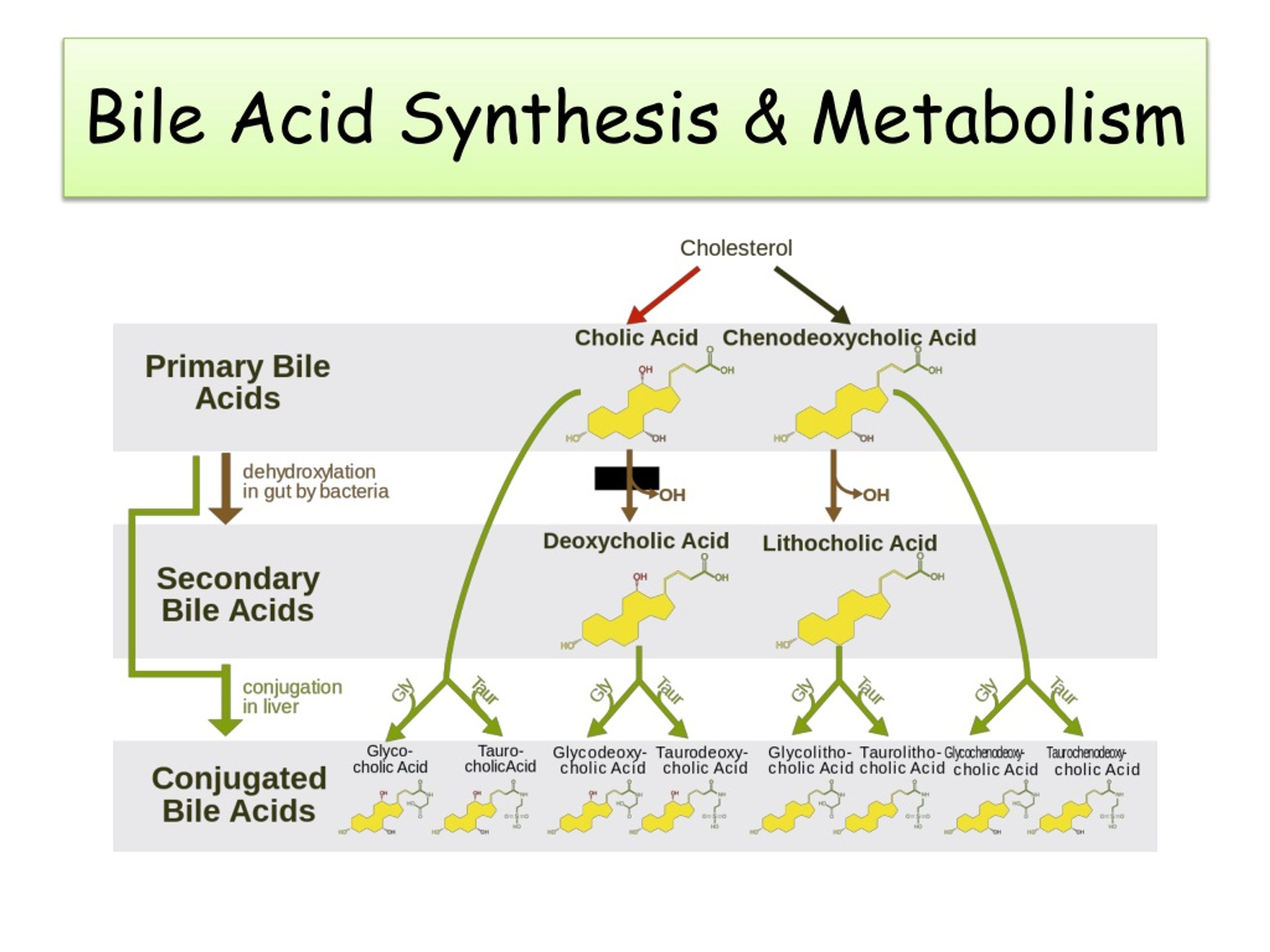
Bile acid metabolism is crucial for the proper functioning of the liver, which plays a significant role in digestion and nutrient absorption. The liver synthesizes bile acids from cholesterol, and these substances act not only as detergents that emulsify fats but also as signaling molecules that regulate various metabolic processes. Disruptions in bile acid homeostasis can lead to significant health issues, including liver diseases and liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding how bile acids function and how their regulation is controlled is essential for developing effective treatment interventions.
Recent research has highlighted the importance of the FXR receptor (Farnesoid X receptor) in maintaining bile acid balance. FXR activation facilitates bile acid excretion and inhibits bile acid production, creating a delicate equilibrium that sustains liver health. When this homeostasis is disrupted, usually through genetic or environmental factors, it can lead to an accumulation of bile acids in the liver. This condition not only causes liver inflammation but also sets the stage for the progression of serious conditions, including liver cancer.
The Role of the YAP Signaling Pathway in Liver Cancer
The YAP signaling pathway has emerged as a vital player in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. Research conducted by Professor Yingzi Yang and her team has shown that YAP, often associated with promoting cell growth, can act as a repressor within the context of bile acid metabolism. By inhibiting FXR, YAP contributes to excessive bile acid production, creating a toxic environment in the liver that leads to fibrosis and ultimately cancer. This counterintuitive role of YAP in liver cancer highlights the complexity of cellular signaling pathways and their implications for liver health.
Targeting the YAP pathway presents a novel intervention strategy for liver cancer treatment. By blocking YAP’s repressive effects on FXR, researchers can potentially enhance bile acid metabolism, leading to reduced liver damage and a decrease in cancer progression. Treatments that stimulate FXR or inhibit YAP’s activity, such as using compounds to activate FXR or increasing bile acid export via BSEP, are being explored as therapeutic avenues. This research opens the door to potential pharmacological advancements that could change the landscape of liver cancer treatment.
Pharmacological Innovations in Liver Cancer Treatment
Current research into pharmacological solutions focuses on stimulating the FXR receptor to regulate bile acid metabolism effectively. By understanding the molecular pathways associated with bile acids, especially in the context of liver cancer, scientists are identifying new therapeutic targets that may lead to improved treatment outcomes. The ability to modulate bile acid levels and re-establish homeostasis could protect the liver from injury and reduce the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Moreover, the development of drugs targeting components of the YAP signaling pathway is gaining traction. By inhibiting YAP’s repressive function, researchers can restore the activity of FXR and promote the proper excretion of bile acids. This line of inquiry represents a significant shift in how liver diseases are treated, moving away from traditional methods and towards a more molecularly-informed approach that could lead to effective interventions for liver cancer and other related conditions.
Implications of Bile Acid Homeostasis for Liver Health
Bile acid homeostasis is critical for maintaining overall liver health and preventing diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. The liver’s ability to produce and recycle bile acids serves multiple functions, from aiding digestion to regulating metabolic processes. An imbalance can lead to pathogenic conditions, indicating the need for further research into the mechanisms that regulate bile acid synthesis and excretion. Understanding these processes not only enhances our knowledge of liver function but also informs strategies for preventing liver diseases.
Restoring bile acid homeostasis is paramount in addressing not just liver cancer but a range of liver-related conditions. Therapies aimed at correcting imbalances in bile acids through lifestyle changes, dietary interventions, or medications that affect FXR or other regulatory pathways have shown promise. By focusing on these areas, healthcare professionals can offer more comprehensive care for patients at risk of liver disease, ultimately improving health outcomes and enhancing quality of life.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Research
Future research in liver cancer is poised to focus significantly on the interplay between bile acids, liver function, and cellular signaling pathways. The insights garnered from studies on the YAP signaling pathway and FXR receptor could lead to groundbreaking therapies. As scientists continue to unravel the complex relationships in bile acid metabolism, new drugs and treatment protocols that target these pathways may emerge, setting a foundation for personalized medicine in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Advancements in technology and molecular research techniques will allow for deeper exploration of the factors influencing bile acid metabolism. By investigating genetic predispositions and environmental factors that contribute to dysregulation, researchers can develop more targeted approaches. The goal is to create effective interventions that prevent not just liver cancer, but also mitigate the broader spectrum of liver diseases, validating the critical role of bile acids in liver health.
The Importance of Early Detection in Liver Cancer
Early detection of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, is crucial for improving treatment outcomes. As studies increasingly highlight the connection between disturbances in bile acid metabolism and the evolution of liver diseases, it becomes imperative to implement screening methods that can identify these changes at an early stage. This approach allows for timely intervention, potentially reversing the course of liver damage before it progresses to cancer.
Innovative diagnostic techniques that monitor bile acid levels and metabolic markers are expected to gain traction in clinical settings. By establishing a standardized method for tracking bile acid homeostasis, healthcare professionals can more readily identify patients at risk for liver cancer. Implementing early detection protocols could significantly enhance survival rates, underscoring the necessity of integrating bile acid metabolism evaluations into routine liver health assessments.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Liver Health
In addition to pharmacological treatments, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis and overall liver health. Diet, physical activity, and avoiding harmful substances (like excessive alcohol) are significant contributors to liver function. For instance, incorporating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support metabolic processes that regulate bile acid production and excretion.
Moreover, managing weight through regular exercise and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can have profound effects on liver function. Obesity is a known risk factor for liver diseases, including HCC, due to its potential to disrupt bile acid metabolism. Educating patients on the importance of these lifestyle choices empowers them to take proactive steps in supporting their liver health and reducing their risk of developing serious conditions.
The Interconnection of Gut Health and Bile Acid Metabolism
The health of the gut microbiome is intrinsically linked to bile acid metabolism, which has significant implications for liver health. The gut microbiota influences the conversion and recycling of bile acids, suggesting that maintaining a balanced microbiome can benefit liver function. Disruptions in gut health can alter bile composition and lead to systemic issues, highlighting the importance of the gut-liver axis in understanding liver diseases and cancer.
Research is ongoing into how dietary interventions that promote gut health, such as prebiotics and probiotics, may improve bile acid metabolism. This relationship underscores the need for a holistic approach to liver health that includes not only pharmacological solutions but also lifestyle and dietary modifications aimed at enhancing gut flora. Ultimately, fostering a healthy microbiome could serve as a protective measure against hepatocellular carcinoma.
The Promise of Gene Therapy in Liver Disease Prevention
Gene therapy represents a novel frontier in preventing and treating liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. By targeting the genetic underpinnings of bile acid metabolism and cellular signaling pathways, such as YAP and FXR, gene therapy could offer personalized solutions for patients at risk. Advances in CRISPR technology and other gene-modifying techniques are paving the way for precise interventions that correct metabolic imbalances.
The potential to modify genes involved in bile acid synthesis and regulation poses exciting opportunities for liver disease prevention. By restoring proper gene function, healthcare providers can mitigate the risks associated with dysregulated bile acid metabolism, thus significantly reducing the chances of developing liver cancers. Continued research into this field will illuminate the viability of gene therapy as a standard treatment option for liver diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does bile acid metabolism relate to liver cancer treatment?
Bile acid metabolism plays a crucial role in liver cancer treatment, specifically for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Imbalances in bile acid levels can contribute to liver diseases, including HCC. Recent studies have identified therapeutic targets, such as the FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) and YAP signaling pathway, which influence bile acid homeostasis and may improve treatment outcomes.
What is the role of FXR in bile acid homeostasis and liver cancer?
The FXR receptor is integral to maintaining bile acid homeostasis. It regulates bile acid production and excretion, preventing excessive accumulation in the liver. Disruption of FXR function due to YAP activation can lead to increased bile acids, causing liver inflammation and potentially contributing to hepatocellular carcinoma.
What is the connection between YAP signaling pathway and bile acid metabolism?
The YAP signaling pathway significantly impacts bile acid metabolism. YAP can act as a repressor of FXR, disrupting bile acid homeostasis and causing excessive bile acid production. This imbalance can lead to liver injury and increase the risk of developing liver cancer, highlighting the YAP-FXR interaction as a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
How can disrupting the YAP-FXR interaction be beneficial in liver cancer treatment?
Disrupting the YAP-FXR interaction may offer therapeutic benefits by restoring proper bile acid metabolism. By enhancing FXR function or inhibiting YAP’s repressive role, it may be possible to reduce bile acid accumulation, liver inflammation, and subsequent tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma.
What recent findings have been made about bile acid metabolism and liver diseases?
Recent research highlights that imbalances in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies indicate that targeting key molecular switches in bile acid regulatory pathways, particularly those involving FXR and YAP, can open new avenues for effective liver cancer treatments.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Linked to liver diseases including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. |
| Key Molecular Switch | Research identifies YAP as a repressor that affects bile acid metabolism. |
| FXR Role | Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is crucial for bile acid homeostasis. YAP activation paralyzes FXR. |
| Consequences of Disruption | Excess bile acids lead to liver fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer. |
| Potential Treatments | Strategies include enhancing FXR function and boosting bile acid excretion. |
| Research Implications | YAP’s role in metabolic control and nutrient sensing has broader implications for liver biology. |
Summary
Bile acid metabolism plays a significant role in liver function and health. Recent research has uncovered the critical impact of bile acid imbalance on liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The identification of YAP as a key molecular switch highlights the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis through mechanisms involving FXR. Understanding these processes opens potential pathways for therapeutic interventions that may reduce the risk of liver cancer, thereby enhancing liver health and overall metabolic regulation.