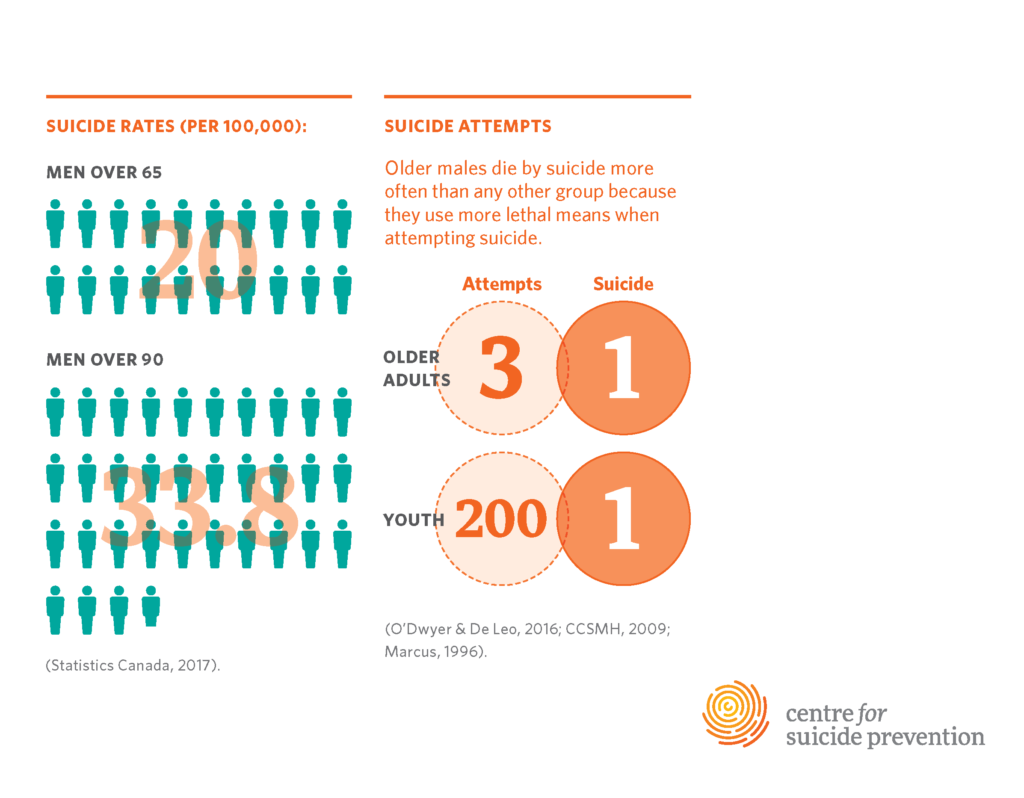
Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent but often overlooked aspect of mental health in aging. Despite holding the highest rates of suicide among all age groups, individuals aged 75 and older face significant barriers in accessing effective resources and support. A recent study underlines that existing suicide prevention efforts are not adequately tailored to meet the unique needs of this demographic, leaving many vulnerable seniors without the assistance they require. This lack of targeted intervention highlights critical suicide risk factors such as social isolation, which disproportionately affect older populations. As mental health initiatives continue to evolve, it’s imperative that we prioritize the development of specialized resources for seniors, including improved online suicide prevention tools, to foster their well-being and safety.
As we delve into the pressing topic of safeguarding the mental health of elderly individuals, it becomes clear that older adults face a distinct set of challenges regarding emotional well-being. Many seniors experience heightened vulnerability to suicidal thoughts, a situation exacerbated by factors such as loneliness and limited access to effective mental health support. Addressing the needs of this population with tailored strategies is not just beneficial but necessary for ensuring their safety and health. There is a pressing demand for resources that cater specifically to the geriatric population, promoting awareness of available treatment options and encouraging dialogue about emotional struggles. Recognizing the importance of enhancing online mental health services for the aging community is a crucial step toward fostering resilience across this demographic.
Understanding Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical area of focus, particularly considering the startling statistics showing that individuals aged 75 and older face the highest suicide rates compared to other age groups. As clinicians emphasize, older adults often grapple with complex mental health issues shaped by social factors such as isolation and the loss of loved ones. These circumstances underline the urgency of providing appropriate resources and support tailored specifically for seniors. Awareness campaigns must address the unique challenges faced by this demographic, ensuring they are insightful, empathetic, and accessible.
Recent studies have indicated that older adults utilize online resources to seek health information, yet they encounter a significant deficit in targeted support for suicide prevention. This highlights the necessity for tailored campaigns directed at older populations, featuring relatable content that addresses their experiences and challenges. Additionally, leveraging digital platforms can help close the gap in accessibility, driving engagement with valuable resources while fostering a supportive community for seniors experiencing mental health struggles. The continued focus on developing relevant interventions will be paramount in reversing tragically elevated suicide rates among older adults.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Mental Health in Aging
Social isolation is one of the most significant risk factors associated with mental health challenges in aging. As individuals reach advanced ages, they may experience increasing detachment from social networks due to factors such as retirement, loss of friends or family, or physical limitations. This isolation often leads to heightened feelings of loneliness and despair, conditions which can precipitate suicidal thoughts. Recognizing social isolation as a vital aspect of mental health in aging can help advocates and healthcare providers design more effective intervention strategies aimed at enhancing social connectedness among seniors.
Tackling the impact of social isolation requires a community-wide effort to foster engagement and support among older adults. Programs that encourage social interaction, such as senior centers, online forums, and community events, can significantly mitigate feelings of loneliness and improve overall well-being. Moreover, integrating technology in these programs can create new opportunities for connection, allowing seniors to interact with others comfortably from their homes. By addressing social isolation in conjunction with mental health services, we can create a holistic approach to improving the quality of life for older adults.
Identifying Suicide Risk Factors in Older Adults
Understanding the specific suicide risk factors in older adults is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies. Factors such as chronic health conditions, cognitive decline, and recent bereavements significantly increase the likelihood of suicidal ideation. Furthermore, societal perceptions – including ageism or the belief that suicidal thoughts are a normal part of aging – can hinder detection and intervention efforts. Thus, mental health professionals and caregivers must be vigilant and educated about identifying these risks, facilitating timely support for seniors who may be vulnerable.
Additionally, it is essential to involve families and communities in the awareness and prevention of suicide risk among older adults. Education on identifying warning signs, fostering open discussions about mental health, and normalizing help-seeking behaviors can empower those closest to seniors to intervene effectively. By creating a safe space for dialogue and support, we can collectively mitigate the stigma around mental health issues in aging, paving the way for a more responsive and understanding healthcare environment.
Essential Resources for Seniors Facing Life Challenges
Access to essential resources for seniors is vital, particularly in the realm of mental health and suicide prevention. Given the unique challenges that older adults face, it is crucial to provide them with accessible knowledge, emotional support, and coping strategies. Available resources may include local mental health services, national helplines, and online platforms equipped with information tailored for seniors, which can empower them to navigate their mental health challenges more effectively. As highlighted in recent studies, there remains a gap in the visibility of such resources, necessitating improved outreach efforts.
Moreover, community organizations and healthcare providers should work toward creating comprehensive resource directories that older adults can easily access and understand. This could include workshops on mental health literacy, hotlines specifically designed for older adults, and informational materials structured in accessible language. By ensuring that these resources are not only available but also truly reachable, we enhance the likelihood that older adults will seek support when experiencing distress, ultimately working to prevent suicides.
The Role of Geriatric Mental Health Professionals
The role of geriatric mental health professionals is pivotal in addressing the intricacies of mental health and suicide prevention among older adults. These specialized clinicians are trained to understand the unique mental health needs of seniors, providing tailored interventions that consider both physical health implications and mental wellness. This integrated approach is essential in the treatment of late-life depression and anxiety, both of which are significant contributors to suicide risk in this demographic.
Moreover, geriatric mental health professionals often serve as advocates for their patients, working to bridge the gap between older adults and the broader healthcare system. By promoting awareness of the mental health issues faced by seniors and facilitating access to appropriate resources, these professionals play a crucial role in combating the stigma associated with aging and mental health care. Their expertise not only aids individuals in crisis but also fosters a more supportive network for seniors navigating mental health challenges.
Promoting Online Suicide Prevention Strategies
In recent years, the surge of technology and digital platforms has opened new avenues for suicide prevention, especially among older adults who may benefit from online resources. Promoting online suicide prevention strategies can provide survivors and at-risk individuals with immediate access to help, support, and information from the comfort of their homes. Effective online initiatives must focus on visibility and accessibility, ensuring that seniors can easily connect with mental health services and find the information they need.
Developing online support systems, such as chat services or virtual support groups designed for older populations, could significantly enhance outreach efforts. Furthermore, tailoring content to address the specific concerns and emotional needs of older adults can empower this demographic to seek help without fear. By harnessing technology to create more inclusive and accessible suicide prevention strategies, we can ensure that older adults receive the critical support they deserve.
Understanding the Importance of Community Engagement
Community engagement plays a fundamental role in addressing mental health issues and suicide prevention among older adults. Through active participation in community programs, seniors can build meaningful connections, reduce feelings of loneliness, and improve their overall mental health. Communities should aim to create inclusive environments where older adults feel valued and supported, fostering greater awareness and dialogue around mental health challenges.
Building community structures that facilitate social support, such as intergenerational programs and volunteer opportunities, can further enrich older adults’ lives. Such initiatives not only combat isolation but also provide proactive avenues for seniors to engage, express their needs, and share their experiences positively. By prioritizing community engagement, we equip older adults with stronger social networks and resilience against mental health challenges.
The Importance of Research in Geriatric Mental Health
Ongoing research in geriatric mental health is crucial for understanding and addressing the unique challenges faced by older adults. By investigating the dynamics of aging, researchers can identify new risk factors, effective interventions, and the best practices for mental health care tailored to this demographic. Current studies underscore the critical need to focus on late-life suicide prevention, considering the societal shifts and the increasing number of seniors.
Additionally, research efforts should involve collaboration across various fields, including psychology, social sciences, and public health, to develop comprehensive strategies aimed at improving mental health outcomes for older adults. Funding initiatives and advocacy for research in this area will significantly contribute to enhancing the understanding of geriatric mental health, ultimately leading to more effective prevention programs, resources, and community support tailored specifically for older adults.
Advocating for Policy Changes to Support Elder Mental Health
Advocating for policy changes to support elder mental health is essential to create a systemic shift in how mental health services are delivered and accessed by older adults. What is needed is a comprehensive approach that not only improves resource allocation but also streamlines care processes across various health systems. Through policy advocacy, stakeholders can work to ensure that seniors’ mental health needs are recognized and prioritized in both public health agendas and funding initiatives.
Moreover, engaging in policy dialogue can empower older adults to voice their experiences and needs directly, ensuring that their perspectives shape the development of mental health services and resources. As we push for systemic changes, it is critical to include a multifaceted approach, integrating mental health services with physical healthcare and community support initiatives. By transforming our policies, we foster a more accommodating and effective framework for addressing the mental health needs of older adults.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the major suicide risk factors for older adults?
Suicide risk factors for older adults include social isolation, chronic health conditions, mental health issues such as depression and anxiety, recent loss of a loved one, and limited access to mental health resources. Understanding these factors can lead to better targeted suicide prevention strategies for older adults.
How can online suicide prevention resources better serve older adults?
Online suicide prevention resources can enhance their effectiveness for older adults by ensuring that content is easily accessible, user-friendly, and specifically tailored to address the unique challenges that seniors face, such as loneliness and declining health.
What strategies can improve geriatric mental health and reduce suicide rates among seniors?
Improving geriatric mental health and reducing suicide rates can involve increasing awareness of mental health resources, enhancing community support networks, fostering social engagement through programs, and providing targeted educational campaigns focused on mental wellness for older adults.
Where can older adults find resources for suicide prevention?
Older adults can find resources for suicide prevention through local mental health organizations, community health centers, and dedicated sections on websites of national organizations that focus on aging and mental health, although accessibility remains a challenge.
What role does social isolation play in suicide prevention for older adults?
Social isolation is a significant risk factor for suicide in older adults. It is crucial to create community initiatives that promote social interaction and help seniors build connections, as these steps can be effective in suicide prevention and improving overall mental health.
What is the importance of tailored suicide prevention programs for seniors?
Tailored suicide prevention programs for seniors are essential because they address the specific needs and circumstances of older adults. These programs can provide targeted interventions, increase awareness of suicide risks within this demographic, and offer appropriate resources to mitigate those risks.
How can family and caregivers support older adults at risk of suicide?
Family and caregivers can support older adults at risk by providing emotional support, encouraging open conversations about mental health, assisting them in accessing healthcare and mental health resources, and involving them in social activities to combat isolation.
What are the signs of suicidal thoughts in older adults?
Signs of suicidal thoughts in older adults may include expressing feelings of hopelessness, withdrawal from social activities, changes in eating or sleeping patterns, increased talk about death, or making arrangements for after one’s death. Recognizing these signs is crucial for timely intervention.
Why is there a need for increased funding for suicide prevention research in older adults?
Increased funding for suicide prevention research in older adults is vital to better understand the unique factors affecting their mental health, develop more effective prevention programs, and ultimately reduce the alarming rates of suicide within this vulnerable population.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Older adults are at highest risk for suicide | Adults aged 75 and older have the highest rates of suicide, with 20.3 per 100,000 according to CDC statistics. |
| Lack of resources targeting older adults | National suicide prevention organizations do not easily provide resources specifically for older adults despite their high risk. |
| Social isolation and loneliness contributing factors | Older adults may be more vulnerable to suicide due to social isolation, loneliness, and underrepresentation in research. |
| Need for tailored prevention programs | Targeted campaigns and tailored prevention programming are necessary to address the specific healthcare needs of older adults. |
| Call for better accessibility of resources | The study urges major organizations to make suicide prevention resources more accessible online for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. The alarming rates of suicide among individuals aged 75 and older highlight a significant gap in available resources tailored to their unique needs. While young adults have seen declines in suicide rates, older adults have not experienced the same relief, emphasizing the importance of targeted prevention strategies. Increased awareness, funding, and research aimed at addressing this imbalance are crucial to safeguard the mental health of our elderly population and ensure they have the support and resources they need.