Drug-resistant antibiotics have emerged as a major global health threat, complicating the treatment of bacterial infections that were once easily manageable. As antibiotic resistance continues to rise, effective treatment options are dwindling, driving scientists and researchers to urgently seek new antibiotics to combat these formidable pathogens. Established firms, like Kinvard Bio, are at the forefront of antibiotic development, innovating compounds that could provide relief against infections which resist conventional treatments. The World Health Organization reports that antibiotic resistance was responsible for over a million deaths in 2019 alone, emphasizing the critical need for new therapeutic strategies. With increased focus on antibiotic discovery and harnessing novel mechanisms of action, the search for solutions to this crisis has never been more vital than now.
The challenge of combating drug-resistant bacteria is commonly referred to as antimicrobial resistance, and it represents a significant threat to public health worldwide. With the rise of resistant pathogens, health innovators are tirelessly working to discover new therapeutic options and improve antibiotic efficacy. Startups like Kinvard Bio are dedicated to pioneering a new class of antibiotics that specifically address the needs brought on by resistant strains. The urgency in developing alternatives has intensified as traditional medications fail against stubborn bacterial infections. By employing cutting-edge research and innovative chemistry, the fight against antibiotic-resistant pathogens is becoming a focal point in medical research and antibiotic development.
Understanding Antibiotic Resistance and Its Consequences
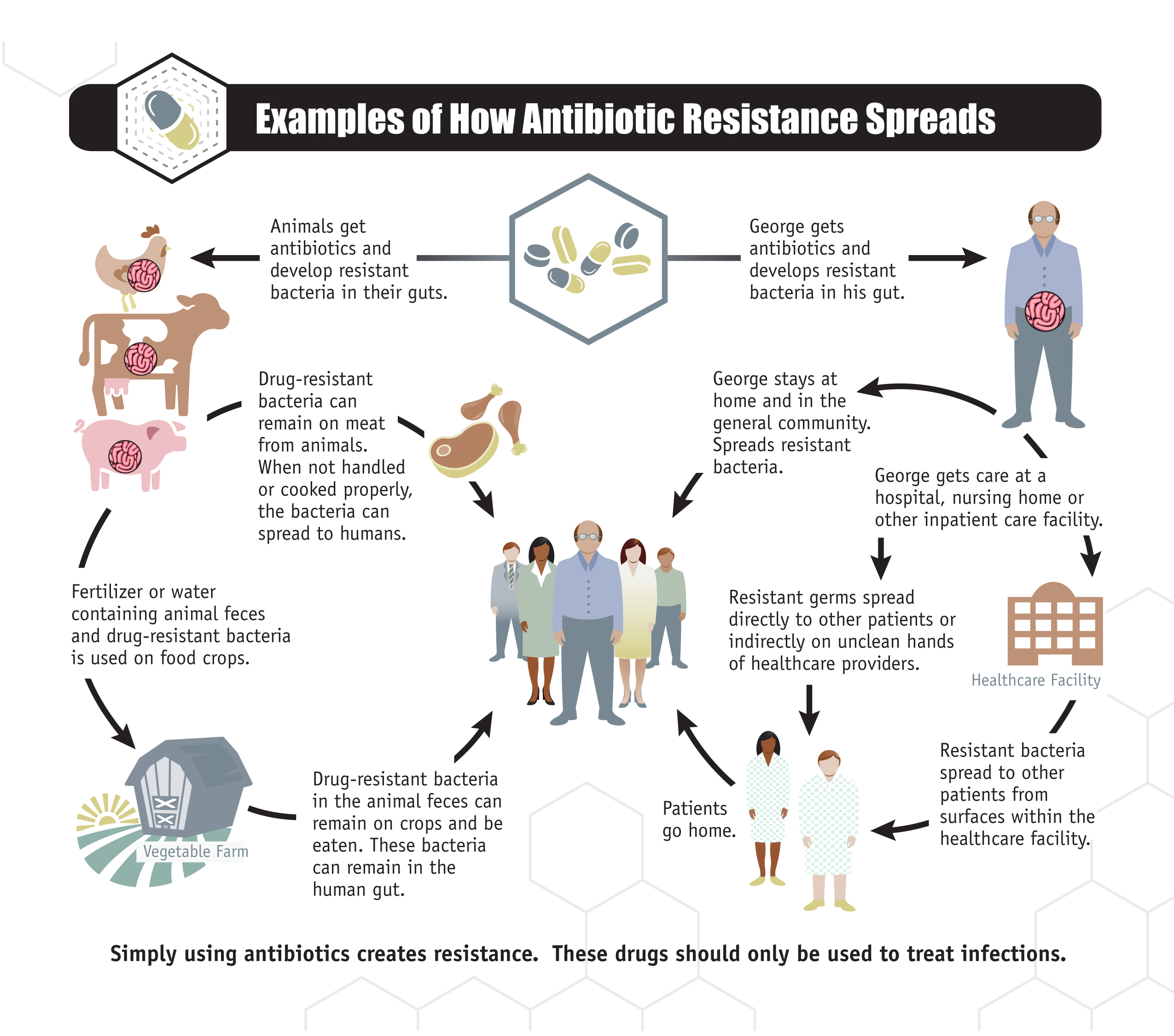
Antibiotic resistance is a growing global health crisis that poses significant threats to effective disease management. As outlined by the World Health Organization, antibiotic resistance was responsible for over a million deaths worldwide in 2019 alone. The inability of doctors to treat common bacterial infections effectively has serious implications for public health, leading to complications in surgery, chemotherapy, and the management of chronic diseases. With drug-resistant bacteria on the rise, the medical community faces a formidable challenge that necessitates the urgent development of new antibiotics.
The mechanisms behind antibiotic resistance are typically adaptive responses by bacteria to survive exposure to antimicrobial agents. This capability allows bacteria to thrive despite the presence of antibiotics that, in earlier times, were potent enough to clear infections. For instance, changes in bacterial cell walls or the development of enzymes that deactivate antibiotics can severely limit treatment options. Continuous misuse and overprescription of antibiotics in both human medicine and agriculture further exacerbate this problem, leading to an alarming rise in drug-resistant infections.
The Role of Kinvard Bio in Developing New Antibiotics
Kinvard Bio stands at the forefront of addressing antibiotic resistance through innovative research and development of new antibiotics. Founded by a team from Harvard University’s Myers Lab, this biotechnology company is pioneering a new class of antibiotics targeting the bacterial ribosome. This approach is particularly promising because the ribosome is an established treatment target in many clinically relevant pathogens. Kinvard’s unique compounds not only show effectiveness against existing resistant bacteria but also aim to evade the mechanisms that make traditional antibiotics ineffective.
The company’s focus on creating structurally preorganized oxepanoprolinamides is indicative of its commitment to overcoming the limitations of previous antibiotic discoveries. As Kinvard Bio’s CEO Lloyd Payne emphasizes, the critical need for novel antibacterials cannot be overstated, especially given the limited pipeline of new antibiotics recently approved. With ongoing support from initiatives like the Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X), Kinvard’s mission aligns with the urgent global need for healthcare innovations that can enhance treatment efficacy against drug-resistant infections.
Innovative Approaches to Antibiotic Development
Kinvard Bio employs a novel strategy in its antibiotic development, focusing on the bacterial ribosome as a target for new drug compounds. This emphasis is crucial as the ribosome plays a vital role in protein synthesis, which is essential for bacterial growth and survival. The new antibiotics being developed by Kinvard are designed to bind effectively to this target, potentially avoiding some of the resistance mechanisms exhibited by previously developed antibiotics. This targeted approach aims to create more effective treatments for various infections that have proven difficult to manage.
The pathway to innovation in antibiotic creation connects deeply with synthetic chemistry, as demonstrated in Kinvard’s lab. The research team’s ability to synthesize new compounds efficiently sets the stage for advancing antibiotic discovery. By customizing molecular structuring, Kinvard aims to unveil antibiotics that can withstand or bypass common resistance profiles. This meticulous attention to chemistry not only fosters new treatment options but also cultivates a new generation of scientists equipped to continue the fight against antibiotic resistance.
The Impact of Drug-Resistant Antibiotics on Public Health
The rise of drug-resistant antibiotics poses a serious risk to public health systems worldwide. Hospitals are becoming battlegrounds where patients with drug-resistant infections are often isolated and treated with older antibiotics that have seen reduced efficacy over time. Such scenarios lead to increased healthcare costs, longer hospital stays, and an uptick in mortality rates. Managing complex infections linked to antibiotic resistance is a challenge that healthcare professionals are grappling with daily, thus intensifying the need for new treatment paradigms.
Furthermore, the implications of drug-resistant antibiotics extend beyond individual patients to entire communities, potentially undermining efforts to control infectious diseases. The emergence of superbugs—bacteria that are resistant to multiple drugs—has made simple infections harder to treat. As the public health landscape continues to evolve under these pressures, initiatives to research and develop effective new antibiotics, such as those being pursued by Kinvard Bio, become paramount. The collaboration between private biotechnology firms and public health organizations is crucial to mitigating this escalating crisis.
Challenges in the Approval of New Antibiotics
Despite the necessity for new antibiotics, the approval rate for innovative treatments has plummeted significantly over the past few decades. Between 2017 and 2022, only a handful of antibiotics were approved, with even fewer emerging from entirely new classes. This stagnation in antibiotic development can be attributed to several factors, including the complexity and expense of clinical trials, compounded by stringent regulatory requirements that companies must navigate. The need for clinical efficacy and safety data places an immense burden on researchers, often discouraging investment in antibiotic discovery.
Moreover, the economic model for antibiotic development presents a unique challenge. Unlike chronic disease medications, antibiotics are typically prescribed for short durations. This leads to lower return on investment for pharmaceutical companies, making them less inclined to develop new antibiotics despite the overwhelming need. To combat this issue, entities like Kinvard Bio are forging strategic alliances with funding organizations to secure the necessary support for their innovative research. Such partnerships are critical to re-energizing the pipeline of new antibiotics and ensuring effective treatments remain available.
Research and Development Innovations at Kinvard Bio
At Kinvard Bio, research and development efforts are geared towards innovating antibiotic solutions that can effectively tackle the burgeoning crisis of antimicrobial resistance. By focusing on the design of compounds that can outsmart existing bacterial defenses, the lab exemplifies a scientific response to a pressing health challenge. The team’s ability to design new antibiotics through targeted chemistry is indicative of a forward-thinking approach that emphasizes both efficacy and safety in drug development.
Furthermore, Kinvard Bio is committed to continuous learning and adaptation in its research methodologies. By drawing on decades of synthetic chemistry advancements, researchers at Kinvard are well-positioned to explore new frontiers in antibiotic development. The insights gleaned from ongoing research not only inform Kinvard’s projects but also contribute to the broader scientific community’s efforts against antibiotic resistance, fostering a spirit of collaboration that is essential for solving such a complex problem.
The Future of Antibiotic Innovation
The future of antibiotic innovation hinges on a multifaceted approach that incorporates not just science but also strategic partnerships and forward-thinking business models. Kinvard Bio is pioneering this approach by engaging extensively with healthcare systems, investors, and regulatory bodies to streamline the development of new antibiotics that can effectively engage resistant bacterial strains. Such collaborations enhance resource utilization and build a cohesive strategy to combat antibiotic resistance.
In addition, as our understanding of bacterial behavior and resistance mechanisms continues to evolve, so too must our strategies for antibiotic development. This means embracing innovative technologies, such as artificial intelligence and advanced screening methods, that can accelerate the drug discovery process. Kinvard Bio’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of conventional antibiotic research exemplifies the proactive stance needed to secure a healthier future for all, ensuring that effective antibiotics remain a cornerstone of modern medicine.
Educational Initiatives in Antibiotic Development
Education plays a pivotal role in addressing the antibiotic resistance crisis by ensuring that the next generation of scientists is well-equipped to tackle this challenge. Kinvard Bio is not only focused on developing new antibiotics but also on fostering collaboration and education within the scientific community. By bringing together emerging scientists and established researchers, the company cultivates knowledge sharing, which is vital for ongoing advancements in antibiotic research.
Moreover, initiatives aimed at raising awareness of antibiotic resistance issues among healthcare professionals and the public are critical. Understanding the risks associated with antibiotic misuse is essential for effective prevention strategies. Kinvard Bio’s commitment to education highlights the company’s vision that combatting antibiotic resistance goes beyond laboratory work—it requires community engagement and informed discussions about the importance of stewardship in antibiotic use.
Global Collaboration to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
Addressing antibiotic resistance requires a concerted global effort involving governments, healthcare organisations, research institutions, and biotechnology firms like Kinvard Bio. Collaboration at an international level facilitates the sharing of information and resources, ultimately accelerating the development of effective antibiotics. By participating in global health initiatives and fostering partnerships, Kinvard is positioned to contribute meaningfully to the fight against drug-resistant infections.
In addition, collaborative efforts enhance the collective response to antibiotic resistance, leading to improved strategies for surveillance, prevention, and treatment. Aligning resources and expertise across borders will ensure that innovative solutions reach those in greatest need. Kinvard Bio embodies this spirit of collaboration, as it seeks to create partnerships that unify efforts against this pressing global health crisis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are drug-resistant antibiotics and why are they a concern?
Drug-resistant antibiotics are antibiotics that are no longer effective against certain bacteria due to antibiotic resistance. This resistance occurs when bacteria evolve mechanisms to resist the drugs designed to kill them, making infections harder to treat. The rise of drug-resistant infections has become a significant health crisis globally, leading to increased morbidity and mortality.
How does antibiotic resistance develop in bacterial infections?
Antibiotic resistance develops in bacterial infections through several mechanisms, such as genetic mutations and the horizontal transfer of resistance genes between bacteria. These changes allow bacteria to survive even when exposed to antibiotics, thereby rendering previously effective treatments useless. This ongoing evolution of bacteria poses a critical challenge for antibiotic development.
What role do new antibiotics play in combating antibiotic resistance?
New antibiotics are essential in combating antibiotic resistance as they provide alternative treatment options against resistant bacteria. Since the development of resistance can render existing antibiotics ineffective, discovering and developing new classes of antibiotics that work through different mechanisms is critical for effective treatment of drug-resistant infections.
What is Kinvard Bio’s approach to developing new antibiotics?
Kinvard Bio focuses on creating a new class of antibiotics called oxepanoprolinamides, which target the bacterial ribosome. This approach aims to exploit differentiated binding mechanisms that may bypass existing resistance to current antibiotic treatments, addressing the urgent need for effective solutions to drug-resistant infections.
How many new antibiotics have been approved recently to tackle antibiotic resistance?
Between 2017 and 2022, only a dozen antibiotics were approved globally, and only two of these belonged to new classes of antibiotics. This low rate of new antibiotic approval highlights the urgent need for innovation in antibiotic development to address the growing challenge of drug-resistant bacteria.
What kind of infections does Kinvard Bio aim to treat with their new antibiotics?
Kinvard Bio aims to treat acute and chronic infections where there is significant unmet medical need, such as bacterial pneumonia, complicated urinary tract infections, and chronic respiratory infections. Their new antibiotics could address infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria, contributing to better patient outcomes.
Why are structured antibiotic compounds like oxepanoprolinamides important?
Structured antibiotic compounds like oxepanoprolinamides are important because they are specifically designed for high-efficiency binding to crucial bacterial targets, such as the ribosome. This targeted approach enhances their effectiveness against a wide range of pathogens and may reduce the likelihood of developing resistance compared to traditional antibiotics.
What funding supports Kinvard Bio’s research and development of new antibiotics?
Kinvard Bio’s research is supported by funding from various sources, including a $1.2 million grant from the Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) and resources from Harvard’s Blavatnik Biomedical Accelerator. This funding facilitates the ongoing development of innovative antibiotics to combat drug-resistant infections.
What are the implications of drug-resistant antibiotics on public health?
The implications of drug-resistant antibiotics on public health are significant. As antibiotic resistance continues to rise, the effectiveness of medical treatments diminishes, leading to longer hospital stays, increased healthcare costs, and a higher risk of mortality from previously treatable infections. Addressing this issue through continued innovation in antibiotic development is crucial for safeguarding public health.
How can healthcare professionals contribute to combatting antibiotic resistance?
Healthcare professionals can contribute to combatting antibiotic resistance by promoting responsible antibiotic prescribing practices, educating patients about the importance of completing prescribed antibiotic courses, and minimizing unnecessary antibiotic use in both humans and agriculture. Furthermore, supporting research initiatives like those at Kinvard Bio can help push forward the development of new antibiotics.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction of Antibiotics | Penicillin, the first antibiotic, revolutionized medicine in the 1940s. |
| Current Situation | Antibiotic resistance has become a major health crisis, leading to millions of deaths. |
| Role of Kinvard Bio | A startup aiming to create new classes of antibiotics to combat resistance. |
| Innovative Approach | Focusing on the bacterial ribosome for targeted antibiotics, with a new compound class called oxepanoprolinamides. |
| Future Goals | Develop both intravenous and oral formulations for treating high unmet medical needs. |
| Research Funding | Support from the National Institutes of Health and CARB-X to advance drug development. |
Summary
Drug-resistant antibiotics have emerged as a critical focus in modern medicine due to the increasing threat posed by antibiotic-resistant infections. As highlighted by Kinvard Bio’s innovative research, the development of novel antibiotics targeting the bacterial ribosome represents a promising solution to this growing crisis. With millions of deaths attributed to antibiotic resistance, the need for effective new treatments has never been more urgent. Kinvard Bio’s dedication to creating these therapeutics could pave the way for more successful treatments and help preserve the efficacy of antibiotics for future generations.