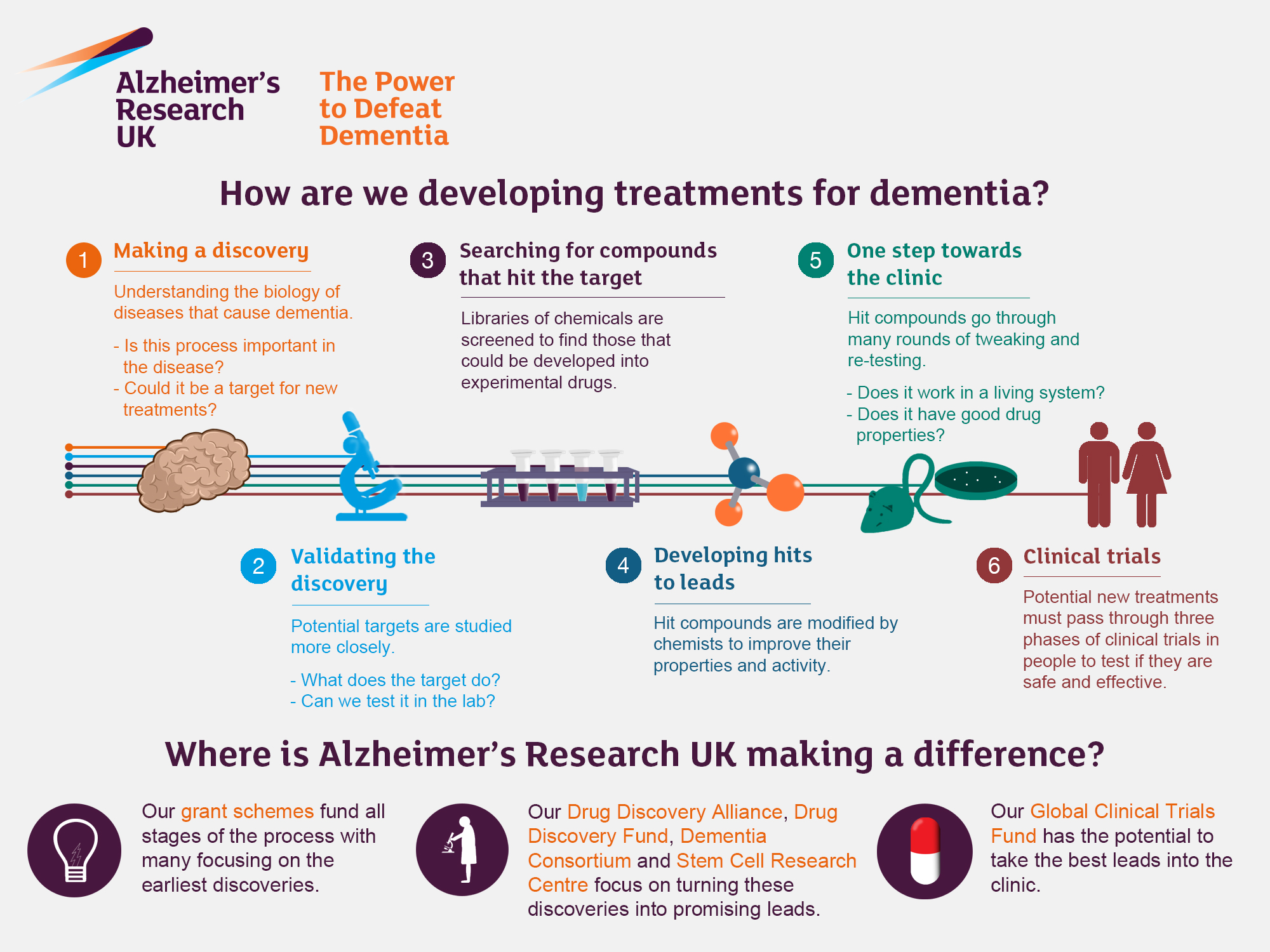
Alzheimer’s research has emerged as a beacon of hope in the battle against one of the most challenging neurodegenerative diseases of our time. With an estimated 7 million Americans currently diagnosed, the urgency for innovative treatments has never been more critical. Pioneering neuroscientist Beth Stevens is at the forefront, revolutionizing our understanding of microglial cells, which function as the brain’s immune system. These cells are responsible for clearing out damaged cells and refining neural connections, but their malfunction can contribute significantly to Alzheimer’s treatment complications. By focusing on this critical aspect of brain health, Stevens’ groundbreaking studies not only pave the way for new therapies but also highlight the intricate relationship between microglial behavior and dementia-related illnesses.
The pursuit of knowledge about Alzheimer’s has opened a dialogue on critical aspects of cognitive decline and its underlying mechanisms. This research encompasses the field of brain health and the roles of immune responses in degenerative conditions. Specifically, the investigation into glial cells, particularly their impact on neural circuitry and disease progression, sheds light on potential interventions for these age-related afflictions. Furthermore, as the scientific community increasingly acknowledges the importance of the brain’s immune system, new avenues for developing preventative and therapeutic strategies are being explored. Understanding these connections is vital for combatting the rising tide of dementia, particularly with the projected increase in cases as populations age.
Understanding Microglial Cells in Alzheimer’s Research
Microglial cells play a crucial role in maintaining brain health as they function as the brain’s immune system. These specialized cells are responsible for monitoring the brain’s environment, responding to injuries, and clearing away dead or damaged cells. In the context of Alzheimer’s disease, research conducted by Beth Stevens and her team highlights how improper functioning of microglia can lead to significant issues, such as abnormal pruning of neural connections. This aberrant activity may exacerbate the effects of neurodegenerative diseases and provide insight into the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s pathology.
Research into microglial cells has opened new avenues for understanding the complexities of neurodegenerative diseases. Stevens’ findings indicate that when microglia do not properly manage synaptic pruning, it can result in the accumulation of toxic proteins associated with Alzheimer’s. This understanding is crucial for developing targeted Alzheimer’s treatments that not only address the symptoms but also correct the underlying cellular dysfunctions. It also underscores the importance of continued research in this field, as microglial activity could potentially serve as a therapeutic target for halting or even reversing the disease’s progression.
The Role of the Brain’s Immune System in Alzheimer’s Treatment
The brain’s immune system, primarily composed of microglial cells, plays an essential role in protecting neuronal health. Beth Stevens emphasizes how understanding this system can lead to innovative Alzheimer’s treatments. By studying how microglia respond to damage and clear out harmful substances, researchers are paving the way for therapies that could enhance the brain’s natural defense mechanisms. This understanding is vital as it provides a framework to explore new treatment modalities that target the immune responses in the brain.
Furthermore, as the population ages and the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease increases, addressing these neurodegenerative conditions becomes increasingly urgent. The insights gained from microglial research may facilitate the identification of new biomarkers for early detection and intervention. This could dramatically alter the trajectory of Alzheimer’s treatment, allowing for earlier diagnosis and more effective management of the disease, ultimately reducing the overall burden on healthcare systems.
Innovations in Alzheimer’s Diagnostics and Biomarkers
Recent breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research have raised hopes for improved diagnostics through the development of new biomarkers. Beth Stevens and her lab’s work with microglial cells has uncovered significant correlations between these immune cells’ activity and the onset of neurodegenerative disease. With a better understanding of microglial function and the pathological processes involved in Alzheimer’s, researchers can identify specific biomarkers that signal the disease’s progression much earlier than traditional methods.
The potential for novel biomarkers to enhance early diagnosis cannot be overstated. Early detection is crucial in Alzheimer’s care, as timely intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for affected individuals. By integrating knowledge of microglial behavior into diagnostic criteria, researchers aim to streamline the identification of Alzheimer’s in patients, leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans. This proactive approach may curtail the staggering costs associated with late-stage Alzheimer’s therapies and ultimately provide a better prognosis for millions.
The Importance of Curiosity-Driven Research in Neuroscience
Curiosity-driven research, like that undertaken by Beth Stevens, is essential for advancing our understanding of complex diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Often, groundbreaking findings stem from basic science that may initially seem disconnected from clinical applications. By pursuing scientific inquiry without immediate practical outcomes in mind, researchers are able to explore fundamental questions that can eventually lead to meaningful innovations in treatment and understanding of diseases.
Stevens’ journey illustrates how seemingly unrelated studies on microglial function can culminate in significant advancements in Alzheimer’s research. The dialogue between basic research and clinical application highlights the importance of funding and support for scientific exploration. The discoveries made in laboratories can lead to transformative changes in how we comprehend and treat neurodegenerative diseases, affirming that all scientific endeavors, even those without immediate results, contribute vital knowledge to the field.
Funding and Support for Alzheimer’s Research
The pursuit of innovative solutions to combat Alzheimer’s requires robust funding and support, particularly in the early stages of research. Beth Stevens has emphasized that much of her groundbreaking work on microglial cells has been possible thanks to significant backing from the National Institutes of Health and other federal agencies. Without such investment, critical research avenues could remain unexplored, stalling potential advancements in understanding and treating Alzheimer’s.
Federal support for neuroscience research not only underpins individual research projects but also fosters collaboration among institutions. This collective effort enhances the exchange of ideas and strategies, promoting a multidimensional approach to combating neurodegenerative diseases. As the aging population grows, continued investment in Alzheimer’s research is crucial for developing effective treatments that can change the lives of millions suffering from this debilitating disease.
Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Research and Treatment
Looking ahead, the future of Alzheimer’s research is increasingly focused on leveraging insights gleaned from microglial studies to develop new treatment strategies. The potential for microglia-targeted therapies could reshape how we treat and prevent Alzheimer’s disease. By understanding how these cells impact neuron health and synaptic function, researchers can tailor interventions to restore proper immune responses within the brain.
Moreover, as research progresses, interdisciplinary approaches combining neuroscience, genomics, and pharmacology will be crucial in developing comprehensive treatment regimens. The goal is to create therapies that not only alleviate symptoms but also address the root causes of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly impacting patient outcomes. Innovations in diagnostic tools and treatments informed by microglial behavior will lead to a brighter future for those affected by Alzheimer’s.
Community Awareness and Advocacy for Alzheimer’s Support
Raising community awareness about Alzheimer’s disease and its impact is paramount in driving support for research initiatives. Increasing public understanding of the importance of microglial research, for instance, can foster greater interest and investment into this crucial area of neuroscience. Advocacy efforts can further highlight the necessity of funding for Alzheimer’s research, urging policymakers to prioritize this pressing health issue affecting millions.
As individuals and organizations rally together to support Alzheimer’s research, the collective voice can lead to significant changes in funding priorities and health policies. Grassroots movements, educational campaigns, and collaborative partnerships can bridge the gap between scientific findings and public knowledge, encouraging a more informed dialogue about Alzheimer’s and its treatment. Such efforts are essential for ensuring that future advancements in research translate into tangible benefits for patients and their families.
The Global Challenge of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease presents a significant global health challenge that transcends borders and cultures. As the prevalence of this neurodegenerative disease rises, nations need to address not only the healthcare implications but also the economic burden it places on society. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, the projected rise in case numbers could lead to staggering healthcare costs, emphasizing the need for immediate and sustained action in research and public health strategies.
The global nature of Alzheimer’s necessitates collaborative international efforts. By sharing research findings, methodologies, and treatment protocols across borders, the scientific community can work together more effectively to tackle the multifaceted aspects of Alzheimer’s research. This collaborative framework will foster a spirit of innovation and urgency, potentially accelerating the development of transformative treatments that can improve the lives of millions affected by this disease worldwide.
The Impact of Aging on Alzheimer’s Disease Prevalence
The aging population is a significant factor contributing to the increasing prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease. As life expectancy continues to rise, more individuals are at risk of developing this debilitating condition. Research indicates that the risk of Alzheimer’s doubles approximately every five years after the age of 65, highlighting the urgent need for targeted research focused on the aging demographic.
Understanding the interplay between aging and Alzheimer’s will be crucial in developing prevention strategies and treatments. Current research aims to uncover the biological mechanics connecting aging with neurodegenerative diseases, particularly how microglial dysfunction in older age may contribute to cognitive decline. Developing interventions to promote brain health in older adults could ameliorate the trajectory of Alzheimer’s and enhance the quality of life in this growing population segment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do microglial cells play in Alzheimer’s research?
Microglial cells are pivotal to Alzheimer’s research as they function as the brain’s immune system. They monitor the brain for illness and injury, clearing out dead or damaged cells and pruning synapses. Aberrant microglial activity has been linked to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, providing a critical area for research and potential treatment.
How does Beth Stevens’ research impact Alzheimer’s treatment?
Beth Stevens’ groundbreaking research has transformed the understanding of microglial cells in Alzheimer’s disease. By studying the role of these cells in synaptic pruning, her lab has provided new insights that could lead to novel biomarkers and therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s treatment, ultimately aiming to improve the lives of millions affected by this neurodegenerative disease.
What is the significance of aberrant pruning in Alzheimer’s disease?
Aberrant pruning refers to the improper removal of synapses by microglial cells, which can lead to neurodegenerative processes associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Research indicates that when pruning goes awry, it might contribute significantly to the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s, highlighting the importance of microglial function in both disease understanding and treatment development.
Why is understanding the brain’s immune system crucial for Alzheimer’s research?
Understanding the brain’s immune system, particularly the role of microglial cells, is crucial for Alzheimer’s research because these cells are involved in maintaining brain health by clearing debris and modulating synaptic connections. Insights into their function may reveal underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease and inspire innovative treatments aimed at enhancing cognitive health.
How has funding influenced Alzheimer’s research, particularly from the NIH?
Funding, especially from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has been essential in advancing Alzheimer’s research. It allows scientists like Beth Stevens to explore complex questions regarding microglial cells and their implications in Alzheimer’s disease, fostering breakthroughs that could lead to effective treatments and improved management strategies for neurodegenerative diseases.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Focus | Beth Stevens’ lab focuses on microglial cells as an immune system in the brain. |
| Microglial Function | Microglia clear dead cells and prune synapses but can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases when pruning is abnormal. |
| Impact on Diseases | Research findings have implications for Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and other disorders. |
| Potential for New Treatments | Stevens’ discoveries could lead to new medications and earlier biomarkers for detection. |
| Funding and Support | Research is significantly supported by federal funding, notably from the NIH. |
| Future Outlook | With the aging U.S. population, Alzheimer’s cases are expected to double by 2050. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s research is vital in understanding and developing solutions for the millions affected by this debilitating disease. Neuroscientist Beth Stevens is pioneering innovations in the study of microglial cells, uncovering their crucial role as the brain’s immune system. Her work contributes significantly to deciphering the complexities of Alzheimer’s, paving the way for future treatments that may alleviate the disease’s impact as the population ages. With projections showing a dramatic increase in Alzheimer’s cases, the importance of this research cannot be overstated.